% Covariance Completion for a mass-spring-damper system % % Written by Armin Zare and Mihailo Jovanovic, April 2016 % % Customized solvers, based on the Alternating Minimization Algorithm (AMA) % and the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM), are used to % solve the Covariance Completion problem (CC) % % minimize -logdetX + gamma*|| Z ||_* (CC) % subject to A*X + X*A' + Z = 0 % E.*(C*X*C') - G = 0 % % A, G, E, L - problem data % X, Z - optimization variables %
clear all
clc
% ================== % MSD system setup % % ================== % number of masses N = 10; % identity and zero matrices I = eye(N); Ibig = eye(2*N); ZZ = zeros(N,N); % forming the state and input matrices T = toeplitz([2 -1 zeros(1,N-2)]); % dynamic matrix A = [ZZ, I; -T, -I]; % input matrix B = [ZZ; I]; % output matrix C = Ibig; % dynamics of the filter that generates colored noise Af = -I; Bf = I; Cf = I; Df = ZZ; % form cascade connection of the plant and the filter Ac = [A, B*Cf; zeros(N,2*N), Af]; Bc = [B*Df; Bf]; % Lyapunov equation for covariance matrix of the cascade systems % P = [X, Y; Y', Z] P = lyap(Ac,Bc*Bc'); % Covariance of the state of the plant Sigma = P(1:2*N,1:2*N);
% ========================================================================= % Structural identity matrix E is formed based on known system correlations % ========================================================================= % structural identity matrix for known elements of covariance matrix Sigma E = [I, I; I, I]; % matrix of known output correlations G = E.*Sigma;
% ================================= % Optimization problem parameters % % ================================= % low-rank parameter gamma gamma = 10; % input options into the optimization procedure options.rho = 10; options.eps_prim = 1.e-6; options.eps_dual = 1.e-6; options.maxiter = 1.e5; % initial conditions Xinit = lyap(A,Ibig); options.Xinit = Xinit; options.Zinit = Ibig; Y1init = lyap(A',-Xinit); options.Y1init = gamma*Y1init/norm(Y1init,2); [n, m] = size(C); options.Y2init = eye(n); options.method = 1; % AMA % options.method = 2; % ADMM
% =================================================================== % optimization procedure -> output = ccama(A,G,E,C,gamma,N,options) % % =================================================================== % Call ccama % % Inputs: (1) dynamic matrix A % matrix of available output correlations G % structural identity matrix E % output matrix C % low-rank parameter gamma % number of masses N % % (2) options % % options.rho - initial step-size % options.eps_prim - tolerance on primal residual % options.eps_dual - tolerance on duality gap % options.maxiter - maximum number of AMA iterations % options.Xinit - feasible initial value for matrix X % options.Zinit - feasible initial value for matrix Z % options.Y1init - dual-feasible initial value for Y1 % options.Y2init - dual-feasible initial value for Y2 % options.method - method = 1, AMA (default) % - method = 2, ADMM % % Outputs: output - structured array containing % % output.X - matrix X resulting from (CC) % output.Z - matrix Z resulting from (CC) % output.Y1 - matrix Y1 resulting from (CC) % output.Y2 - matrix Y2 resulting from (CC) % output.Jp - primal objective function at each step % output.Jd - dual objective function at each step % output.Rp - primal residual at each step % output.dg - duality gap at each step % output.steps - number of steps for solving (CC) % output.time - cumulative solve time (in seconds) per outer iteration % output.flag - flag = 0, iteration counter reaches its max % flag = 1, problem is solved before maxiter steps % tic output = ccama(A,C,E,G,gamma,n,m,options); time = toc;
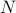
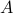 ;
;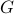 of available correlations and the structural identity
of available correlations and the structural identity 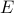 ;
; ;
;