function output = ccama(A,C,E,G,gamma,n,m,options)
if nargin < 7
error('At least six input arguments are required.')
elseif nargin == 7
options.rho = 10;
options.eps_prim = 1.e-5;
options.eps_dual = 1.e-4;
options.maxiter = 1.e5;
Xinit = lyap(A,eye(m));
options.Xinit = Xinit;
options.Zinit = eye(m);
Y1init = lyap(A',-Xinit);
options.Y1init = gamma*Y1init/norm(Y1init,2);
options.Y2init = eye(n);
options.method = 1;
elseif nargin > 8
error('Too many input arguments.')
end
rho0 = options.rho;
eps_prim = options.eps_prim;
eps_dual = options.eps_dual;
MaxIter = options.maxiter;
X = options.Xinit;
Z = options.Zinit;
Y1 = options.Y1init;
Y2 = options.Y2init;
if options.method == 1
eigLadY = real(eig( A'*Y1 + Y1*A + C'*(E.*Y2)*C ));
logdetLadY = sum(log(eigLadY));
dualY = logdetLadY - trace(G*Y2) + m;
Ibig = eye(m);
beta = 0.5;
rho1 = rho0;
bbfailures = [];
fprintf('%s %s %s %s %s %s %s\n------------------------------------------------------------------------------ \n',...
'rho_BB', ' rho', ' eps_prim',' res_prim', ' eps_dual',...
' abs(eta)',' iter');
tic
for AMAstep = 1 : MaxIter,
Xnew = (A'*Y1 + Y1*A + C'*(E.*Y2)*C)\Ibig;
Xnew = (Xnew + Xnew')/2;
eigX = real(eig(Xnew));
logdetX = sum(log(eigX));
gradD1 = A*Xnew + Xnew*A';
gradD2 = E.*(C*Xnew*C') - G;
Rnew2 = gradD2;
rho = rho1;
for j = 1:50,
a = gamma/rho;
Wnew = -(A*Xnew + Xnew*A' + (1/rho)*Y1);
[U,S,V] = svd(Wnew);
Svec = diag(S);
Svecnew = ( (1 - a ./ abs(Svec)) .* Svec ) .* (abs(Svec) > a);
Znew = U*diag(Svecnew)*V';
Znew = (Znew + Znew')/2;
Rnew1 = gradD1 + Znew;
Y1new = Y1 + rho*Rnew1;
Y2new = Y2 + rho*Rnew2;
Y1new = (Y1new + Y1new')/2;
Y2new = (Y2new + Y2new')/2;
eigLadYnew = real(eig( A'*Y1new + Y1new*A + C'*(E.*Y2new)*C ));
logdetLadYnew = sum(log(eigLadYnew));
dualYnew = logdetLadYnew - trace(G*Y2new) + m;
if min(eigLadYnew) < 0
rho = rho*beta;
elseif (dualYnew < dualY + ...
trace(gradD1*(Y1new - Y1)) + ...
trace(gradD2*(Y2new - Y2)) - ...
(0.5/rho)*norm(Y1new - Y1,'fro')^2 - ...
(0.5/rho)*norm(Y2new - Y2,'fro')^2)
rho = rho*beta;
else
break;
end
end
Rnew1 = A*Xnew + Xnew*A' + Znew;
Rnew2 = E.*(C*Xnew*C') - G;
res_prim = sqrt(norm(Rnew1,'fro')^2 + norm(Rnew2,'fro')^2);
eta = -logdetX + gamma*sum(Svecnew) - dualYnew;
if mod(AMAstep,100) == 0
disp([num2str(rho1,'%6.1E'),' ', ...
num2str(rho,'%6.1E'),' ', ...
num2str(eps_prim,'%6.1E'),' ' ...
num2str(res_prim,'%6.1E'),' ' ...
num2str(eps_dual,'%6.1E'),' ' ...
num2str(abs(eta),'%6.1E'),' ', ...
num2str(AMAstep,'%i')])
end
Xnew1 = (A'*Y1new + Y1new*A + C'*(E.*Y2new)*C)\Ibig;
Xnew1 = (Xnew1 + Xnew1')/2;
gradD1new = A*Xnew1 + Xnew1*A';
gradD2new = E.*(C*Xnew1*C') - G;
rho1 = real(( norm(Y1new - Y1,'fro')^2 + norm(Y2new - Y2,'fro')^2)/ ...
(trace((Y1new - Y1)*(gradD1-gradD1new)) + trace((Y2new - Y2)*(gradD2-gradD2new))));
if rho1 < 0 || isnan(rho1)
rho1 = rho0;
bbfailures(end+1) = AMAstep;
end
output.Jp(AMAstep) = -log(det(Xnew)) + gamma*norm_nuc(Znew);
output.Jd(AMAstep) = real(dualYnew);
output.Rp(AMAstep) = res_prim;
output.dg(AMAstep) = abs(eta);
output.time(AMAstep) = toc;
if (abs(eta) < eps_dual && res_prim < eps_prim)
disp('AMA converged to assigned accuracy!!!')
disp(strcat('AMA steps: ',num2str(AMAstep)))
disp([num2str(rho1,'%6.1E'),' ', ...
num2str(rho,'%6.1E'),' ', ...
num2str(eps_prim,'%6.1E'),' ' ...
num2str(res_prim,'%6.1E'),' ' ...
num2str(eps_dual,'%6.1E'),' ' ...
num2str(abs(eta),'%6.1E'),' ', ...
num2str(AMAstep,'%i')])
break;
end
Y1 = Y1new;
Y2 = Y2new;
dualY = dualYnew;
end
if AMAstep == MaxIter
output.flag = 0;
else
output.flag = 1;
end
output.X = Xnew;
output.Z = Znew;
output.Y1 = Y1new;
output.Y2 = Y2new;
output.steps = AMAstep;
elseif options.method == 2
V = rand(m,m);
V = (V + V')/2;
eigVmin = min(real(eig(V)));
if eigVmin < 0,
V = 2*abs(eigVmin)*eye(m) + V;
end
V = V/norm(V,'fro');
maxit = 100;
eigMax = zeros(maxit,1);
for ind = 1:maxit,
Y1p = A*V + V*A';
Y2p = E.*(C*V*C');
Vnew = A'*Y1p + Y1p*A + C'*Y2p*C;
eigMax(ind) = trace(V*Vnew);
V = Vnew/norm(Vnew,'fro');
end
clear Y1p Y2p V
rho = rho0;
mu = 2*rho*eigMax(end);
a = gamma/rho;
fprintf('%s %s %s %s %s %s\n----------------------------------------------------------------------------- \n',...
'rho',' eps_prim',' res_prim', ' eps_dual',...
' abs(eta)',' iter');
tic
for ADMMstep = 1 : MaxIter,
U1 = -(Z + (1/rho)*Y1);
U2 = G - (1/rho)*Y2;
for indX = 1:20
AadAX = A'*(A*X + X*A') + (A*X + X*A')*A + C'*(E.*(C*X*C'))*C;
RHS = mu*X - rho*AadAX + rho*(A'*U1 + U1*A + C'*(E.*U2)*C);
[Vrhs,Drhs] = eig(RHS);
Lvec = diag(Drhs);
xvec = Lvec/(2*mu) + sqrt( (Lvec/(2*mu)).^2 + 1/mu );
Xnew = Vrhs*diag(xvec)/Vrhs;
Xnew = (Xnew + Xnew')/2;
X = Xnew;
end
Wnew = -(A*Xnew + Xnew*A' + (1/rho)*Y1);
[U,S,V] = svd(Wnew,0);
Svec = diag(S);
Svecnew = ( (1 - a ./ abs(Svec)) .* Svec ) .* (abs(Svec) > a);
Znew = U*diag(Svecnew)*V';
Znew = (Znew + Znew')/2;
Rnew1 = A*Xnew + Xnew*A' + Znew;
Rnew2 = E.*(C*Xnew*C') - G;
res_prim = sqrt(norm(Rnew1,'fro')^2 + norm(Rnew2,'fro')^2);
res_dual = rho*norm(A'*(Znew-Z)+(Znew-Z)*A,'fro');
Y1new = Y1 + rho*Rnew1;
Y2new = Y2 + rho*Rnew2;
eigLadYnew = real(eig( A'*Y1new + Y1new*A + C'*(E.*Y2new)*C ));
logdetLadYnew = sum(log(eigLadYnew));
dualYnew = logdetLadYnew - trace(G*Y2new) + m;
eigX = real(eig(Xnew));
logdetX = sum(log(eigX));
eta = -logdetX + gamma*sum(Svecnew) - dualYnew;
if mod(ADMMstep,100) == 0
disp([num2str(rho,'%6.1E'),' ', ...
num2str(eps_prim,'%6.4E'),' ' ...
num2str(res_prim,'%6.4E'),' ' ...
num2str(eps_dual,'%6.4E'),' ' ...
num2str(abs(eta),'%6.1E'),' ', ...
num2str(ADMMstep,'%i')])
end
output.Jp(ADMMstep) = -log(det(Xnew)) + gamma*norm_nuc(Znew);
output.Jd(ADMMstep) = real(dualYnew);
output.Rp(ADMMstep) = res_prim;
output.dg(ADMMstep) = abs(eta);
output.time(ADMMstep) = toc;
if (abs(eta) < eps_dual && res_prim < eps_prim)
disp('ADMM converged to assigned accuracy!!!')
disp(strcat('ADMM steps: ',num2str(ADMMstep)))
disp([num2str(rho,'%6.1E'),' ', ...
num2str(eps_prim,'%6.4E'),' ' ...
num2str(res_prim,'%6.4E'),' ' ...
num2str(eps_dual,'%6.4E'),' ' ...
num2str(abs(eta),'%6.1E'),' ', ...
num2str(ADMMstep,'%i')])
break;
end
X = Xnew;
Z = Znew;
Y1 = Y1new;
Y2 = Y2new;
a1 = 10;
t1 = 2;
if res_prim > a1*res_dual
rho = rho * t1;
a = gamma/rho;
elseif res_dual > a1*res_prim
rho = rho / t1;
a = gamma/rho;
end
end
if ADMMstep == MaxIter
output.flag = 0;
else
output.flag = 1;
end
output.X = Xnew;
output.Z = Znew;
output.Y1 = Y1new;
output.Y2 = Y2new;
output.steps = ADMMstep;
end
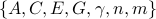 and the input options and returns the solution to the covariance completion problem (CC). Here,
and the input options and returns the solution to the covariance completion problem (CC). Here, 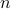 and
and 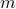 denote the number of the states and the outputs, respectively. Input options allows users to specify the following parameters:
denote the number of the states and the outputs, respectively. Input options allows users to specify the following parameters: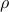 ;
;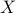 ;
;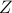 ;
;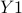 ;
;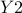 ;
;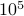 ;
;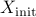 =
= 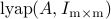 ,
,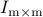 ;
;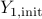 =
= 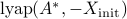 ,
,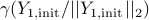 ;
;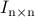 ;
;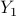 resulting from the optimization problem (CC);
resulting from the optimization problem (CC);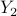 resulting from the optimization problem (CC);
resulting from the optimization problem (CC);