SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR (part 2)
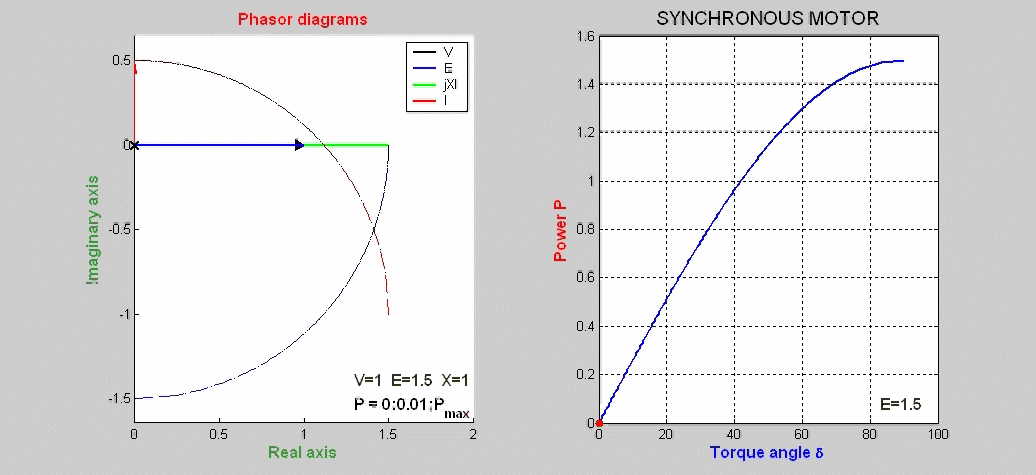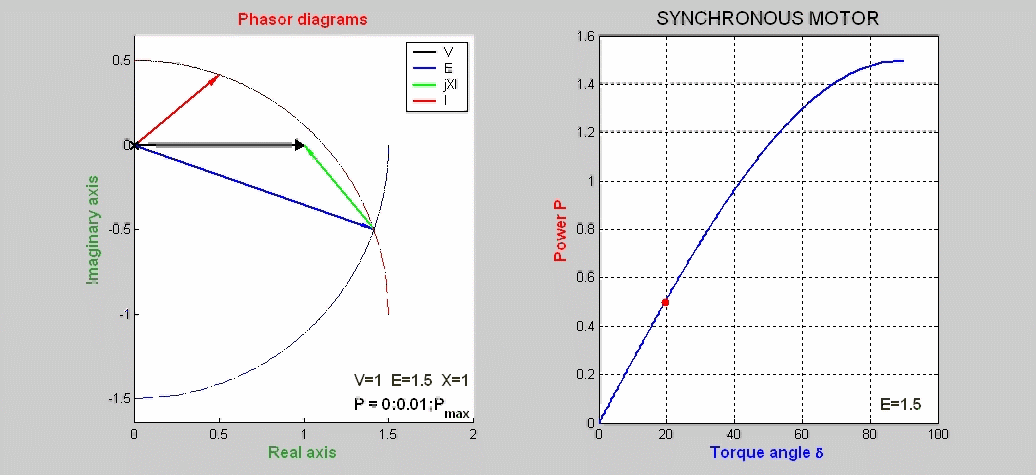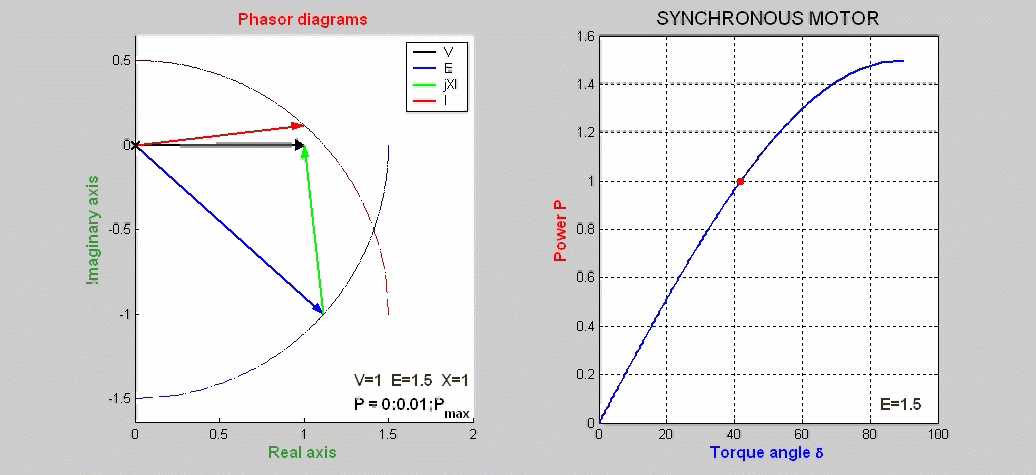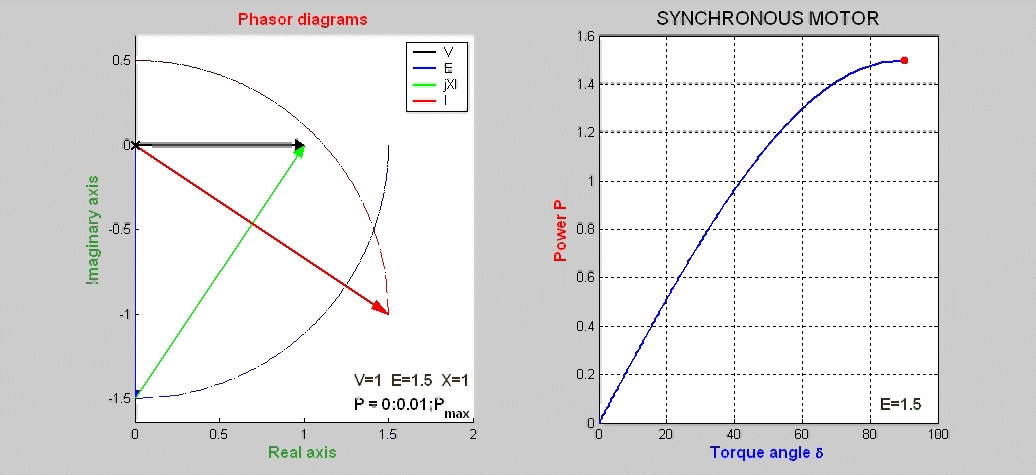
The steady-state characteristics of a synchronous motor
represented by phasor diagrams are shown as function
of the load P with the excitation voltage E kept constant.
The power expression is P = I V cos(φ) = E V sin(δ) / X. The basic phasor
equation is V = E + jX I.
The locus of E is a portion
of a circle of radius E centered at the origin of the complex plane.
The locus of I is also a
circle of radius E/X centered on the imaginary axis at –V/X.
The power P versus the torque angle δ is also plotted.